The world of finance is a dynamic environment in which many significant events for the entire society are constantly taking place. Therefore, every person planning to trade on the forex exchange should be ready to learn all the new information about these phenomena.
The decision of the сentral bank of a particular country to pursue a quantitative easing policy significantly affects the processes taking place in FX. Therefore, if you know the features of this event, you can benefit from the situation.
How?
Quantitative Easing (QE) is an irregular monetary policy decision where central banks buy long-term securities to increase the money supply in the economy. Central banks are the main participants of the FX where they can change the currency value in the most effective way. However, the main aim of the central banks is to control the economy by changing policies.
The typical action by the central bank is to point to an interest rate hike when inflation is low and decrease the interest rate when inflation is high. By doing so, the bank can control the buying power of money following the change in the economy.
Besides taking basic actions, QE is a way to control the money supply when the economy faces an adverse situation.
Let’s have a look in detail at how the QE affects the FX.
What is QE?
It is one kind of monetary policy where the central bank purchases long-term bonds and securities that usually increase the money supply to the economy.
When the central bank (CB) buys securities, it adds new money to the economy, and the additional money helps lower the interest rate by reducing fixed-income securities. Thus, another aim of the QE program is to expand the balance sheet of the central bank.
When the short-term interest rate comes to zero or moves to zero, the traditional approach of the CB to target the interest rate becomes less effective. In that case, the CB targets to buy assets with some specific amount. As a result, the program will increase the money supply to the economy, and banks will get more liquidity.
The Federal Reserve started the QE program after the 2008 market crash, but other CB began to stimulate the economy.
Let’s have a look at a comparative chart of QE programs among major central banks.
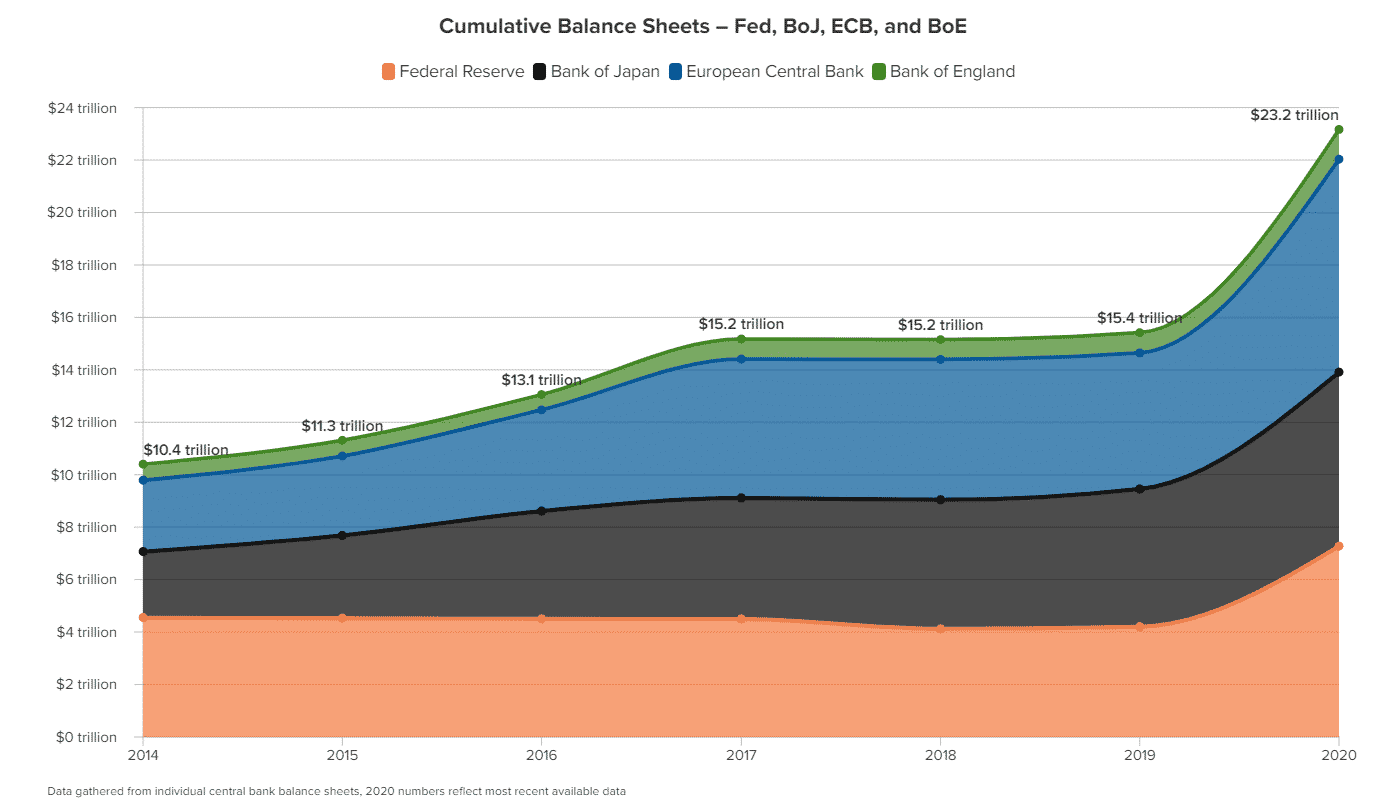
Examples of the QE
QE became familiar to the world of CB as soon as the Federal Reserve announced its first program during the financial crisis of 2008. At that time, the Federal Funds rate was near zero, and the Fed focused on ensuring financial stability during the global financial crisis.
As a result, the Fed purchased many government bonds to lower borrowing costs and support the economy. However, due to the decision, the economy got the power to increase the translation with printed money that ultimately raised inflation.
Other examples of the QE program:
- During the Asian financial crisis in 1997, Japan faced an economic recession that led the Bank of Japan to start an aggressive quantitative easing program to increase the money supply to the economy. The Bank of Japan started to buy government bonds, private debts, and stocks. The effect of the QE program was negative for the economy, where the Japanese GDP fell from $5.45 trillion to $4.52 trillion due to the QE program.
- The most recent example of the QE is the $700 billion asset purchase program initiated by the Federal Reserve to aid the economy during the Covid pandemic. The virus infection rate started to rise, and the government was forced to initiate lockdown and business closure that affected the economy negatively.
How does QE affect the FX?
The FX is where investors can buy/sell currencies required to run their businesses or make a profit. The profit from the FX comes with the change in the currency value.
At the beginning of 2010, the EUR/USD price was 1.43, changing to 1.11 in 2020. Therefore, if you took a sell trade in 2010, you would make a considerable profit in 2020. But the question is why the EUR/USD price fell from 1.43 to 1.11?
The answer is simple. It is a supply and demand game where the increase in supply makes the currency weaker, and an increase in demand makes money stronger.
As it is the global market, there are many reasons behind the change in supply and demand for every currency where the QE program plays an important role:
- The central bank prints money and buys financial assets with it. As a result, the money supply to the economy increases.
- The increase in the money supply means an increase in supply or decrease in demand. As a result, the currency has a higher possibility to be weaker against its pair.
Let’s have a look at an example.
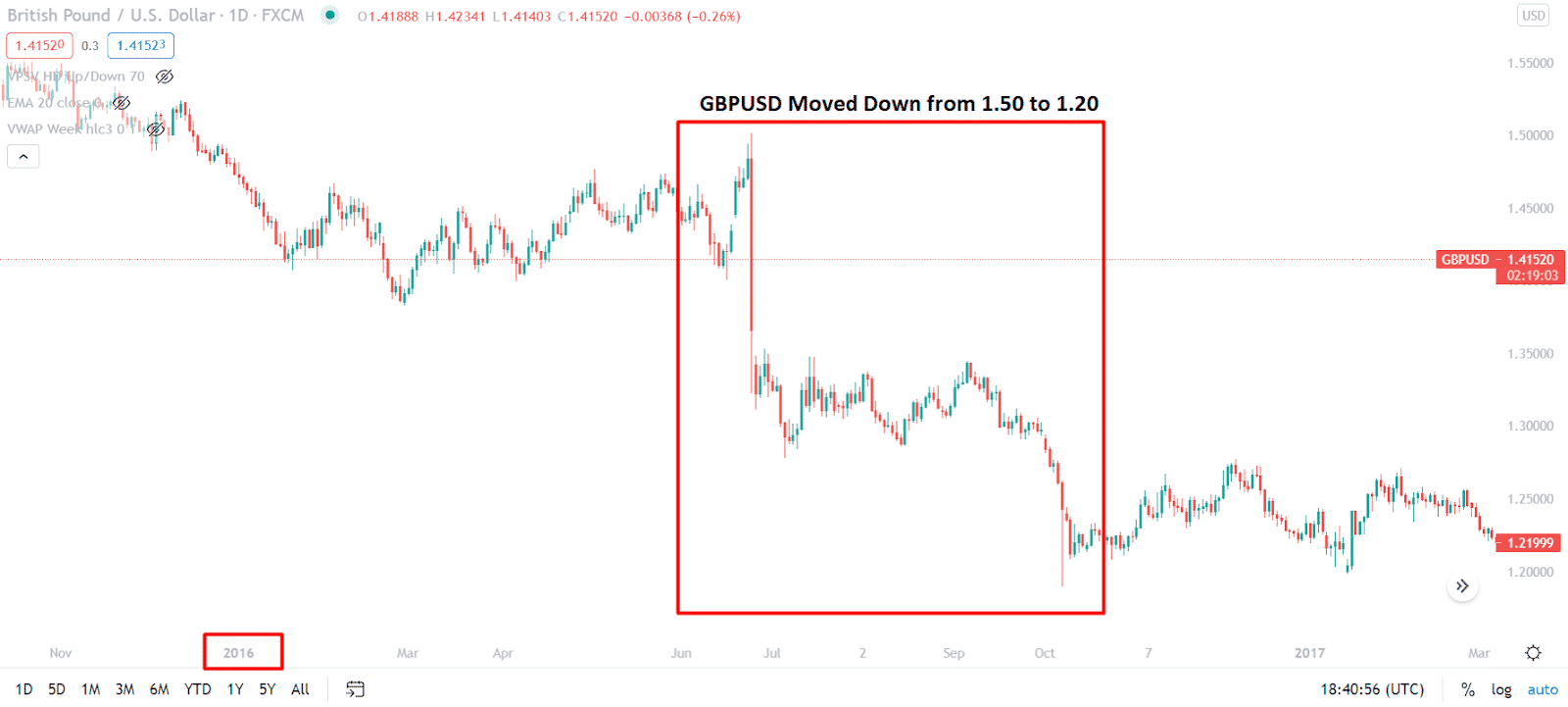
The above image shows that the GBPUSD price moved down from 1.50 to 1.20 level in 2016.
At that time, the Bank of England launched a further QE program to aid the economy for the economic ramification of Brexit. The Bank of England took a plan to buy 60 billion pounds of bonds and 10 billion corporate debts. As a result, the interest rate increased, and the economy got investment and employment from the QE program. On the other hand, due to the oversupply, GBP/USD moved down aggressively.
Conclusion: how to trade the QE?
The QE works as a significant trend identifier for a currency pair. Based on the past price action analysis, every currency faced bearish pressure as soon as the QE program was initiated. However, announcing a QE program does not mean that traders should jump into the trade immediately.
FX requires a systematic approach where traders should follow some rules with solid risk management. In every trading strategy, if the trade direction comes towards the trend, it becomes profitable.
In that case, you can consider QE as a tool to identify the market direction besides using traditional technical analysis.